This story was originally published by The Current GA.
Birds Georgia is looking for coastal volunteers who don’t mind getting up early and aren’t squeamish. Their task will be to walk a predetermined route once a week in downtown Savannah or downtown Brunswick looking for birds that have had a fatal encounter with a building.
Birds Georgia was previously called Georgia Audubon and remains an affiliate of the National Audubon Society. Its Project Safe Flight Georgia studies bird-into-building crashes across the state. The project is entering its ninth year, but just expanded to the coast in 2023.
“Birds Georgia launched Project Safe Flight in 2015 to gain a better understanding of the bird-building collision problem across Georgia,” Adam Betuel, Birds Georgia’s director of conservation said in a prepared statement. “We have been studying what species are most likely to collide with buildings, how many birds are affected, and what parts of the state are most problematic. Since the program began, we’ve learned a lot about how and where building collisions are occurring, and we’ve implemented some programs and changes to help reduce collisions and make Georgia safer for migrating birds.”
Researchers estimate between 350 million and 1 billion birds perish each year from colliding with buildings in the U.S.
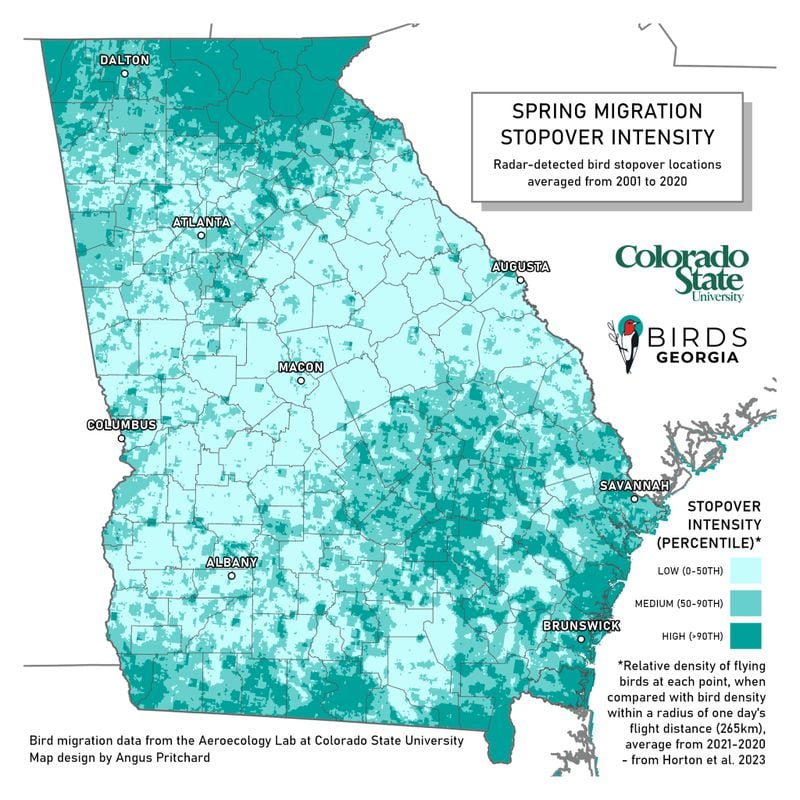
The coastal program focuses on Savannah and Brunswick. Both cities have what research has shown is a dangerous combination for birds: low-rise building of 3-12 stories and plenty of trees.
Credit: Birds Georgia
Credit: Birds Georgia
“It’s mostly the reflection of vegetation against the glass that is the actual cause of the collision,” said Sarah Tolve, coastal conservation coordinator for Birds Georgia, in an interview with The Current GA. “So Savannah, being a Tree City, there’s lots of trees surrounding lots of buildings, and the birds just don’t see that as a barrier. So they’re running into them in the early morning hours after settling down to feed, and then getting out to go. They just hit what they think is a tree, but is very much glass solid surface.”
Birds Georgia is looking for volunteers who can commit to at least one day a week, one to two hours per shift. Guided by an app, volunteers will walk the route shortly after sunrise. Along with the downtowns, there’s also a route in the College of Coastal Georgia. Fewer than 10 coastal volunteers are currently enrolled.
“What they’re looking for is birds that are either stunned or already dead,” Tolve said. “We ask that they go out pretty early in the morning to help beat scavengers and other cleanup crews, like people, business owners that may clean off their front windows and things like that. When you find a bird, you document it, and put it through our database.”
Part of the documentation involves collecting specimens in good condition and depositing them in drop box freezers — either at the UGA Marine Education Center and Aquarium on Skidaway or the UGA Marine Extension Service in Brunswick. Researchers will examine the birds to determine what they’ve been eating and their health before the collision.
The monitoring season officially kicks off March 15 and runs through May 31, but help will be most needed in April and early May. The fall migration season runs August 15 through November 15.
Since the program began in 2015, volunteers have collected data from more than 4,200 birds representing 135 different species that perished after colliding with buildings. Statewide, volunteers most often find ruby-throated hummingbirds, followed by Tennessee warblers, Swainson’s thrushes, cedar waxwings, and ovenbirds. Yellow-bellied sapsuckers, wood thrushes, American robins, common yellowthroats, and red-eyed vireos round out the 10 most commonly collected species by Project Safe Flight volunteers.
To sign up as a Project Safe Flight Volunteer, learn how to make your home bird-safe, or to report dead birds you find at your home or workplace, visit https://www.birdsgeorgia.org/project-safe-flight.html.
Along with volunteering, there are several other ways the public can help. One of the easiest is to reduce nighttime lighting during peak migration periods. The Lights Out Georgia program encourages homeowners and commercial properties to turn off nighttime lights from midnight to 6 a.m. during peak migration. New migration forecasting technology allows Birds Georgia to predict nights of extremely high bird migration and issue Lights Out Alerts for evenings of peak migratory activity. For more information or to sign up, visit https://www.birdsgeorgia.org/lights-out-georgia.html.
Birds Georgia will host a Project Safe Flight webinar at 7 p.m. April 9 to share information about bird-building collisions and causes, and to discuss ways we can make our homes and cities safer. Sign up here.
Credit: The Current GA
Credit: The Current GA
MEET OUR PARTNER
This story comes from our partner, The Current GA, an inclusive nonprofit, independent news organization which provides in-depth watchdog journalism for Savannah and Coastal Georgia’s communities. Sign up for their newsletter here.
If you have any feedback or questions about our partnerships, you can contact Senior Manager of Partnerships Nicole Williams via email at nicole.williams@ajc.com.